[논문] 바이오 나노복합체를 이용한 맞춤형 약물 방출 시스템에 관한 리뷰(Multifunctional PLA/Gelatin B…
페이지 정보
- Date : 23-01-20 14:06
- Views : 5,351 time
관련링크
본문
[논문]
"Multifunctional PLA/Gelatin Bionanocomposites for Tailored Drug Delivery Systems"
27 May 2022
Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1138
Carmen Moya-Lopez, Alberto Juan, Murillo Donizeti, Jesus Valcarcel, José A. Vazquez,
Eduardo Solano, David Chapron, Patrice Bourson, Ivan Bravo, Carlos Alonso-Moreno,
Pilar Clemente-Casares, Carlos Gracia-Fernández, Alessandro Longo, Georges Salloum-Abou-Jaoude,
Alberto Ocaña, Manuel M. Piñeiro, Carolina Hermida-Merino, Daniel Hermida-Merino
[Abstract]
A series of bionanocomposites composed of shark gelatin hydrogels and PLA nanoparticles
featuring different nanostructures were designed to generate multifunctional drug delivery systems
with tailored release rates required for personalized treatment approaches.
The global conception of the systems was considered from the desired customization of the drug release
while featuring the viscoelastic properties needed for their ease of storage and posterior local administration
as well as their biocompatibility and cell growth capability for the successful administration at the biomolecular level.
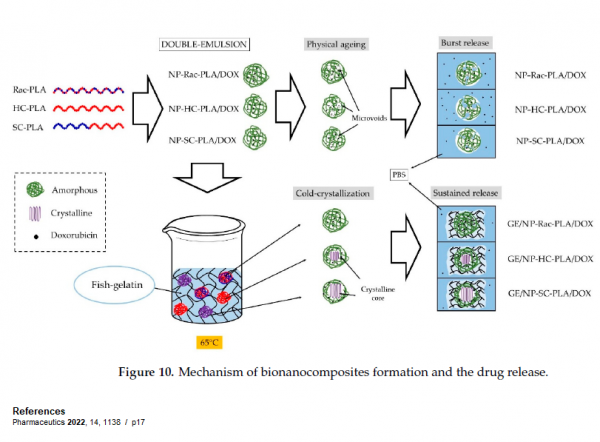
The hydrogel matrix offers the support to develop a direct thermal method to convert the typical kinetic trapped
nanostructures afforded by the formulation method whilst avoiding the detrimental nanoparticle agglomeration
that diminishes their therapeutic effect.
The nanoparticles generated were successfully formulated with two different antitumoral compounds (doxorubicin and dasatinib)
possessing different structures to prove the loading versatility of the drug delivery system.
The bionanocomposites were characterized by several techniques (SEM, DLS, RAMAN, DSC,SAXS/WAXS and rheology)
as well as their reversible sol–gel transition upon thermal treatment that occurs during the drug delivery system preparation and the thermal annealing step.
In addition, the local applicability of the drug delivery system was assessed by the so-called “syringe test” to validate both the storage capability
and its flow properties at simulated physiological conditions.
Finally, the drug release profiles of the doxorubicin from both the PLA nanoparticles or the bionanocomposites
were analyzed and correlated to the nanostructure of the drug delivery system.
본 논문은 맞춤형 약물 방출률(속도)을 제어하기 위하여
다양한 나노구조를 특징으로 하는 젤라틴 하이드로겔과 PLA 나노입자로 구성된 바이오 나노복합체를 이용\한
다기능 약물전달시스템의 설계에 관한 연구이다.
전반적으로 생체분자 수준에서 성공적인 투여를 위한 생체적합성 및 세포 성장 능력 뿐만 아니라
약물의 저장 및 국소 투여의 용이성에 필요한 점탄성 특성을 유지하여 맞춤형 약물방출을 할 수 있는지를 고려하였다.
하이드로겔 매트릭스는 치료 효과를 감소시키는 유해한 나오입자의 응집을 막고 열을 이용하여 나노구조를 변환하는 방법을 제시하였다.
생성된 나노입자에 독소루비신과 다사티닙을 성공적으로 제형화함으로써 약물로딩의 다양성을 검증하였다.
바이오 나노복합체는 SEM, DLS, RAMAN, DSC, SAXS/WAXS, 유동학, 어닐링 등의 기술을 통해 특성화 되었다.
약물전달 시스템의 적용 가능성은 시물레이션된 생리학적 조건에서 저장 능력과 흐름 특성을 모두 검증하기 위해 주사기 테스트를 진행하였다.
마지막으로, PLA 나노입자 또는 바이오나노복합체 로부터의 독소루비신의 약물 방출 프로파일을 분석하고 약물 전달 시스템의 나노구조와 연관시켰다.